* [PUBLISHER] upload files #175 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-19-symmetric-key-encryption.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #177 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-19-symmetric-key-encryptio.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #178 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #179 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #180 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #181 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #182 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #183 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #184 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #185 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #186 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #187 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 14. Secure Multiparty Computation.md * DELETE FILE : _posts/Lecture Notes/Modern Cryptography/2023-09-19-symmetric-key-encryption.md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #188 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 14. Secure Multiparty Computation.md * DELETE FILE : _posts/Lecture Notes/Modern Cryptography/2023-09-19-symmetric-key-encryption.md * chore: remove files * [PUBLISHER] upload files #197 * PUSH NOTE : 수학 공부에 대한 고찰.md * PUSH NOTE : 09. Lp Functions.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-09.png * PUSH NOTE : 08. Comparison with the Riemann Integral.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-08.png * PUSH NOTE : 04. Measurable Functions.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-04.png * PUSH NOTE : 06. Convergence Theorems.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-06.png * PUSH NOTE : 07. Dominated Convergence Theorem.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-07.png * PUSH NOTE : 05. Lebesgue Integration.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-05.png * PUSH NOTE : 03. Measure Spaces.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-03.png * PUSH NOTE : 02. Construction of Measure.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-02.png * PUSH NOTE : 01. Algebra of Sets and Set Functions.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-01.png * PUSH NOTE : Rules of Inference with Coq.md * PUSH NOTE : 블로그 이주 이야기.md * PUSH NOTE : Secure IAM on AWS with Multi-Account Strategy.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : separation-by-product.png * PUSH NOTE : You and Your Research, Richard Hamming.md * PUSH NOTE : 10. Digital Signatures.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-10-dsig-security.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-10-schnorr-identification.png * PUSH NOTE : 9. Public Key Encryption.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-09-ss-pke.png * PUSH NOTE : 8. Number Theory.md * PUSH NOTE : 7. Key Exchange.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-07-dhke.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-07-dhke-mitm.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-07-merkle-puzzles.png * PUSH NOTE : 6. Hash Functions.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-06-merkle-damgard.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-06-davies-meyer.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-06-hmac.png * PUSH NOTE : 5. CCA-Security and Authenticated Encryption.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-05-ci.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-05-etm-mte.png * PUSH NOTE : 1. OTP, Stream Ciphers and PRGs.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-01-prg-game.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-01-ss.png * PUSH NOTE : 4. Message Authentication Codes.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-04-mac.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-04-mac-security.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-04-cbc-mac.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-04-ecbc-mac.png * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-03-ecb-encryption.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-03-cbc-encryption.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-03-ctr-encryption.png * PUSH NOTE : 2. PRFs, PRPs and Block Ciphers.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-02-block-cipher.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-02-feistel-network.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-02-des-round.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-02-DES.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-02-aes-128.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-02-2des-mitm.png * PUSH NOTE : 18. Bootstrapping & CKKS.md * PUSH NOTE : 17. BGV Scheme.md * PUSH NOTE : 16. The GMW Protocol.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-16-beaver-triple.png * PUSH NOTE : 15. Garbled Circuits.md * PUSH NOTE : 14. Secure Multiparty Computation.md * PUSH NOTE : 13. Sigma Protocols.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-13-sigma-protocol.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-13-okamoto.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-13-chaum-pedersen.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-13-gq-protocol.png * PUSH NOTE : 12. Zero-Knowledge Proofs (Introduction).md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-12-id-protocol.png * PUSH NOTE : 11. Advanced Topics.md * PUSH NOTE : 0. Introduction.md * PUSH NOTE : 02. Symmetric Key Cryptography (1).md * PUSH NOTE : 09. Transport Layer Security.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-09-tls-handshake.png * PUSH NOTE : 08. Public Key Infrastructure.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-08-certificate-validation.png * PUSH NOTE : 07. Public Key Cryptography.md * PUSH NOTE : 06. RSA and ElGamal Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 05. Modular Arithmetic (2).md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-03-feistel-function.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-03-cfb-encryption.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-03-ofb-encryption.png * PUSH NOTE : 04. Modular Arithmetic (1).md * PUSH NOTE : 01. Security Introduction.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-01-cryptosystem.png * PUSH NOTE : Search Time in Hash Tables.md * PUSH NOTE : 랜덤 PS일지 (1).md * chore: rearrange articles * feat: fix paths * feat: fix all broken links * feat: title font to palatino
29 KiB
share, toc, math, categories, path, tags, title, date, github_title, image, attachment
| share | toc | math | categories | path | tags | title | date | github_title | image | attachment | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| true | true | true |
|
_posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography |
|
13. Sigma Protocols | 2023-11-07 | 2023-11-07-sigma-protocols |
|
|
The previous 3-coloring example certainly works as a zero knowledge proof, but is quite slow, and requires a lot of interaction. There are efficient protocols for interactive proofs, we will study sigma protocols.
Sigma Protocols
Definition
Definition. An effective relation is a binary relation
\mc{R} \subset \mc{X} \times \mc{Y}, where\mc{X},\mc{Y},\mc{R}are efficiently recognizable finite sets. Elements of\mc{Y}are called statements. If(x, y) \in \mc{R}, thenxis called a witness fory.
Definition. Let
\mc{R} \subset \mc{X} \times \mc{Y}be an effective relation. A sigma protocol for\mc{R}is a pair of algorithms(P, V)satisfying the following.
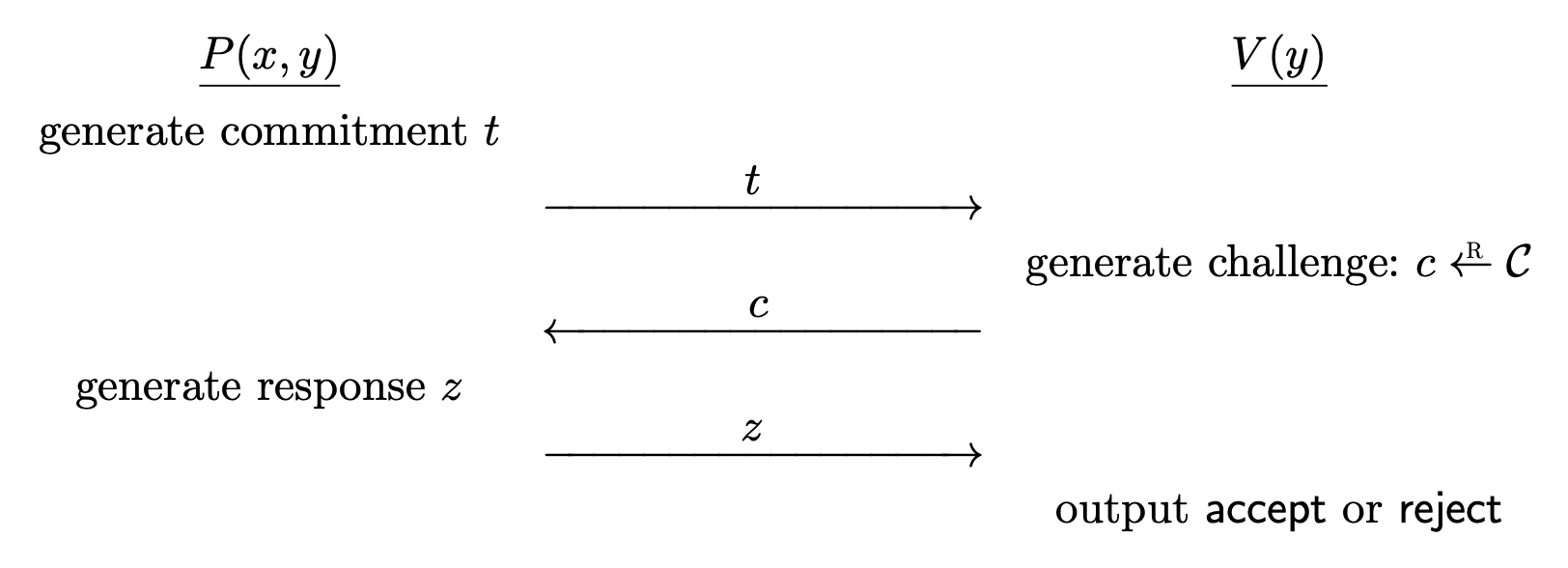
- The prover
Pis an interactive protocol algorithm, which takes(x, y) \in \mc{R}as input.- The verifier
Vis an interactive protocol algorithm, which takesy \in \mc{Y}as input, and outputs\texttt{accept}or\texttt{reject}.The interaction goes as follows.1
Pcomputes a commitment messagetand sends it toV.Vchooses a random challengec \la \mc{C}from a challenge space and sends it toP.Pcomputes a responsezand sends it toV.Voutputs either\texttt{accept}or\texttt{reject}, computed strictly as a function of the statementyand the conversation(t, c, z).For all
(x, y) \in \mc{R}, at the end of the interaction betweenP(x, y)andV(y),V(y)always outputs\texttt{accept}.
- The verifier is deterministic except for choosing a random challenge
c \la \mc{C}. - If the output is
\texttt{accept}, then the conversation(t, c, z)is an accepting conversation fory. - In most cases, the challenge space has to be super-poly. We say that the protocol has a large challenge space.
Soundness
The soundness property says that it is infeasible for any prover to make the verifier accept a statement that is false.
Definition. Let
\Pi = (P, V)be a sigma protocol for\mc{R} \subset \mc{X}\times \mc{Y}. For a given adversary\mc{A}, the security game goes as follows.
- The adversary chooses a statement
y^{\ast} \in \mc{Y}and gives it to the challenger.- The adversary interacts with the verifier
V(y^{\ast}), where the challenger plays the role of verifier, and the adversary is a possibly cheating prover.The adversary wins if
V(y^{\ast})outputs\texttt{accept}buty^{\ast} \notin L _ \mc{R}. The advantage of\mc{A}with respect to\Piis denoted\rm{Adv} _ {\rm{Snd}}[\mc{A}, \Pi]and defined as the probability that\mc{A}wins the game.If the advantage is negligible for all efficient adversaries
\mc{A}, then\Piis sound.
Special Soundness
For sigma protocols, it suffices to require special soundness.
Definition. Let
(P, V)be a sigma protocol for\mc{R} \subset \mc{X} \times \mc{Y}.(P, V)provides special soundness if there is an efficient deterministic algorithm\rm{Ext}, called a knowledge extractor with the following property.Given a statement
y \in \mc{Y}and two accepting conversations(t, c, z)and(t, c', z')withc \neq c',\rm{Ext}outputs a witness (proof)x \in \mc{X}such that(x, y) \in \mc{R}.
The extractor efficiently finds a proof x for y \in \mc{Y}. This means, if a possibly cheating prover P^{\ast} makes V accept y with non-negligible probability, then P^{\ast} must have known a proof x for y. Thus P^{\ast} isn't actually a dishonest prover, he already has a proof.
Note that the commitment t is the same for the two accepting conversations. The challenge c and c' are chosen after the commitment, so if the prover can come up with z and z' so that (t, c, z) and (t, c', z') are accepting conversations for y, then the prover must have known x.
We also require that the challenge space is large, the challenger shouldn't be accepted by luck.
Special Soundness \implies Soundness
Theorem. Let
\Pibe a sigma protocol with a large challenge space. If\Piprovides special soundness, then\Piis sound.For every efficient adversary
\mc{A},\rm{Adv} _ {\rm{Snd}}[\mc{A}, \Pi] \leq \frac{1}{N}where
Nis the size of the challenge space.
Proof. Suppose that \mc{A} chooses a false statement y^{\ast} and a commitment t^{\ast}. It suffices to show that there exists at most one challenge c such that (t^{\ast}, c, z) is an accepting conversation for some response z.
If there were two such challenges c, c', then there would be two accepting conversations for y^{\ast}, which are (t^{\ast}, c, z) and (t^{\ast}, c', z'). Now by special soundness, there exists a witness x for y^{\ast}, which is a contradiction.
Special Honest Verifier Zero Knowledge
The conversation between P and V must not reveal anything.
Definition. Let
(P, V)be a sigma protocol for\mc{R} \subset \mc{X} \times \mc{Y}.(P, V)is special honest verifier zero knowledge (special HVZK) if there exists an efficient probabilistic algorithm\rm{Sim}(simulator) that satisfies the following.
- For all inputs
(y, c) \in \mc{Y} \times \mc{C},\rm{Sim}(y, c)outputs a pair(t, z)such that(t, c, z)is always an accepting conversation fory.- For all
(x, y) \in \mc{R}, letc \la \mc{C}and(t, z) \la \rm{Sim}(y, c). Then(t, c, z)has the same distribution as the conversation betweenP(x, y)andV(y).
The difference is that the simulator takes an additional input c. Also, the simulator produces an accepting conversation even if the statement y does not have a proof.
Also note that the simulator is free to generate the messages in any convenient order.
The Schnorr Identification Protocol Revisited
The Schnorr identification protocol is actually a sigma protocol. Refer to Schnorr identification protocol (Modern Cryptography) for the full description.
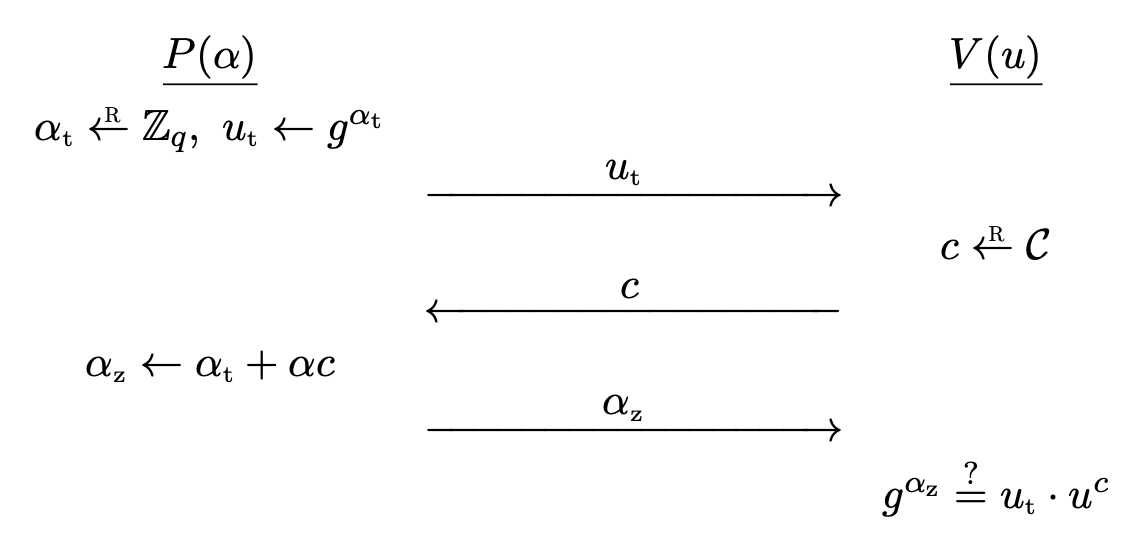
The pair
(P, V)is a sigma protocol for the relation\mc{R} \subset \mc{X} \times \mc{Y}where\mc{X} = \bb{Z} _ q, \quad \mc{Y} = G, \quad \mc{R} = \left\lbrace (\alpha, u) \in \bb{Z} _ q \times G : g^\alpha = u \right\rbrace.The challenge space
\mc{C}is a subset of\bb{Z} _ q.
The protocol provides special soundness. If (u _ t, c, \alpha _ z) and (u _ t, c', \alpha _ z') are two accepting conversations with c \neq c', then we have
g^{\alpha _ z} = u _ t \cdot u^c, \quad g^{\alpha _ z'} = u _ t \cdot u^{c'},
so we have g^{\alpha _ z - \alpha _ z'} = u^{c - c'}. Setting \alpha^{\ast} = (\alpha _ z - \alpha _ z') /(c - c') satisfies g^{\alpha^{\ast}} = u, solving the discrete logarithm and \alpha^{\ast} is a proof.
As for HVZK, the simulator chooses \alpha _ z \la \bb{Z} _ q, c \la \mc{C} randomly and sets u _ t = g^{\alpha _ z} \cdot u^{-c}. Then (u _ t, c, \alpha _ z) will be accepted. Note that the order doesn't matter. Also, the distribution is same, since c and \alpha _ z are uniform over \mc{C} and \bb{Z} _ q and the choice of c and \alpha _ z determines u _ t uniquely. This is identical to the distribution in the actual protocol.
Dishonest Verifier
In case of dishonest verifiers, V may not follow the protocol. For example, V may choose non-uniform c \in \mc{C} depending on the commitment u _ t. In this case, the conversation from the actual protocol and the conversation generated by the simulator will have different distributions.
We need a different distribution. The simulator must also take the verifier's actions as input, to properly simulate the dishonest verifier.
Modified Schnorr Protocol
The original protocol can be modified so that the challenge space \mc{C} is smaller. Completeness property is obvious, and the soundness error grows, but we can always repeat the protocol.
As for zero knowledge, the simulator \rm{Sim} _ {V^{\ast}}(u) generates a verifier's view (u, c, z) as follows.
- Guess
c' \la \mc{C}. Samplez' \la \bb{Z} _ qand setu' = g^{z'}\cdot u^{-c'}. Sendu'toV^{\ast}. - If the response from the verifier
V^{\ast}(u')iscandc \neq c', restart.c = c'holds with probability1 / \left\lvert \mc{C} \right\lvert, sincec'is uniform.
- Otherwise, output
(u, c, z) = (u', c', z').
Sending u' to V^{\ast} is possible because the simulator also takes the actions of V^{\ast} as input. The final output conversation has distribution identical to the real protocol execution.
Overall, this modified protocol works for dishonest verifiers, at the cost of efficiency because of the increased soundness error. We have a security-efficiency tradeoff.
But in most cases, it is enough to assume honest verifiers, as we will see soon.
Other Sigma Protocol Examples
Okamoto's Protocol
This one is similar to Schnorr protocol. This is used for proving the representation of a group element.
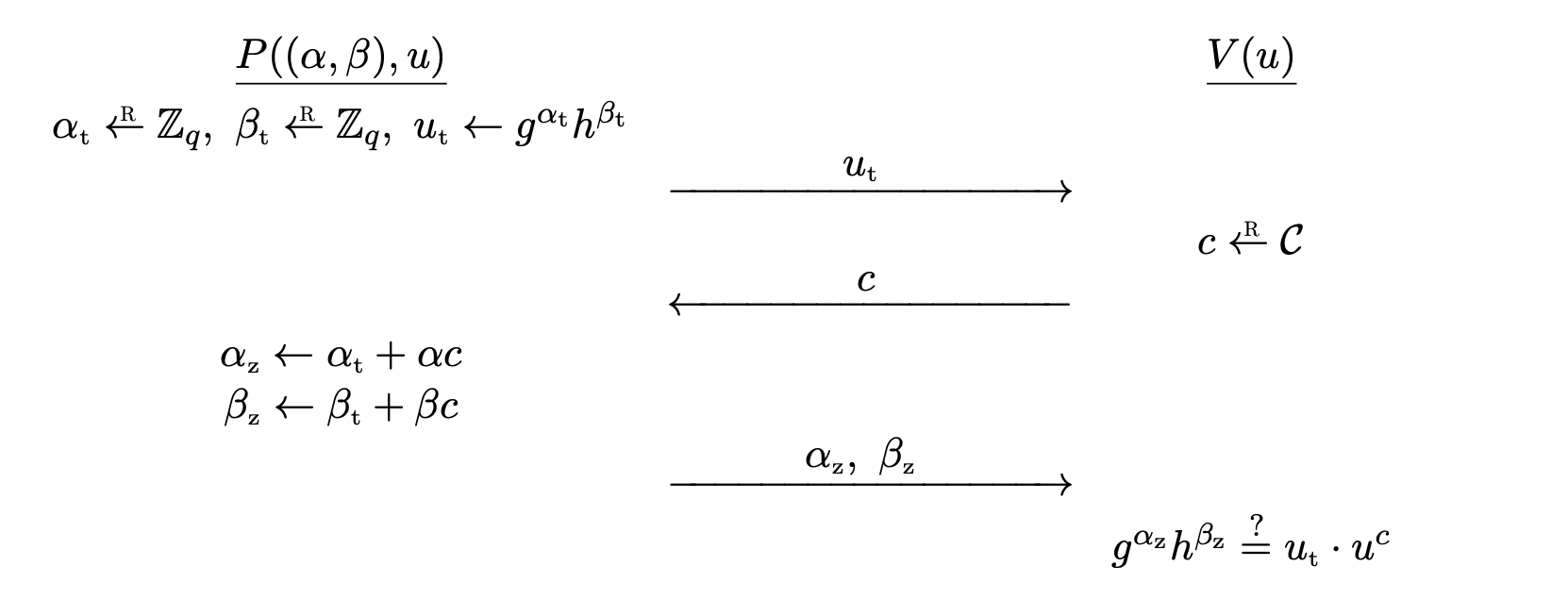
Let G = \left\langle g \right\rangle be a cyclic group of prime order q, let h \in G be some arbitrary group element, fixed as a system parameter. A representation of u relative to g and h is a pair (\alpha, \beta) \in \bb{Z} _ q^2 such that g^\alpha h^\beta = u.
Okamoto's protocol for the relation
\mc{R} = \bigg\lbrace \big( (\alpha, \beta), u \big) \in \bb{Z} _ q^2 \times G : g^\alpha h^\beta = u \bigg\rbrace
goes as follows.
Pcomputes random\alpha _ t, \beta _ t \la \bb{Z} _ qand sends commitmentu _ t \la g^{\alpha _ t}h^{\beta _ t}toV.Vcomputes challengec \la \mc{C}and sends it toP.Pcomputes\alpha _ z \la \alpha _ t + \alpha c,\beta _ z \la \beta _ t + \beta cand sends(\alpha _ z, \beta _ z)toV.Voutputs\texttt{accept}if and only ifg^{\alpha _ z} h^{\beta _ z} = u _ t \cdot u^c.
Completeness is obvious.
Theorem. Okamoto's protocol provides special soundness and is special HVZK.
Proof. Very similar to the proof of Schnorr. Refer to Theorem 19.9.2
The Chaum-Pedersen Protocol for DH-Triples
The Chaum-Pederson protocol is for convincing a verifier that a given triple is a DH-triple.
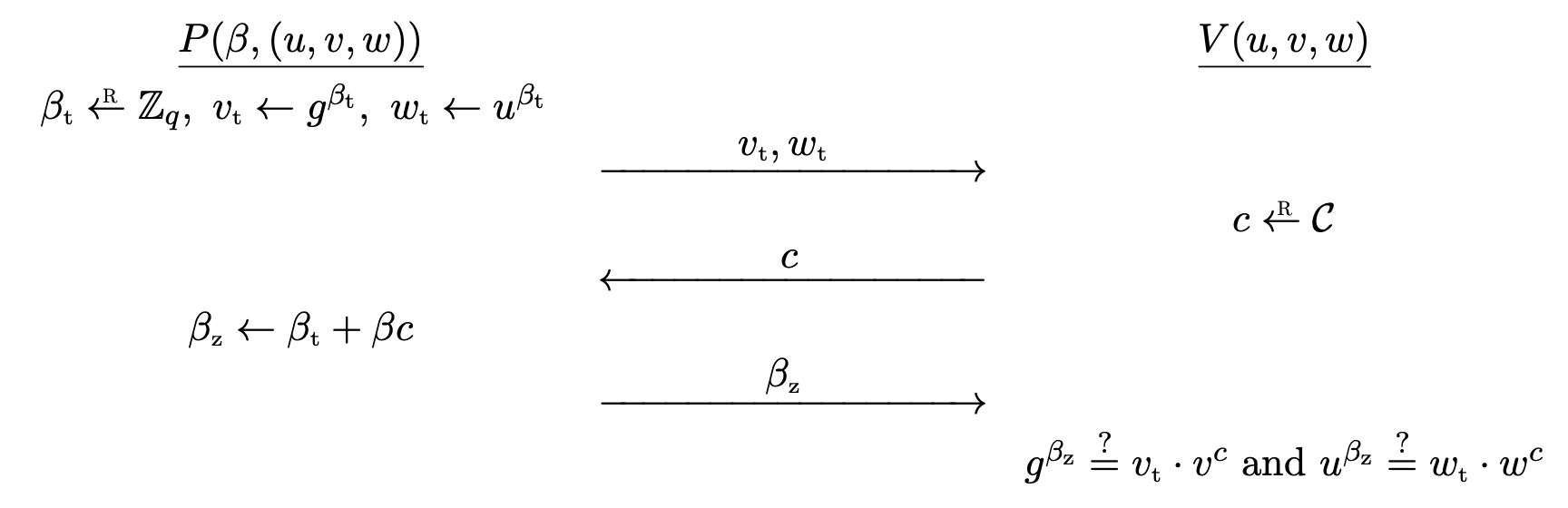
Let G = \left\langle g \right\rangle be a cyclic group of prime order q. (g^\alpha, g^\beta, g^\gamma) is a DH-triple if \gamma = \alpha\beta. Then, the triple (u, v, w) is a DH-triple if and only if v = g^\beta and w = u^\beta for some \beta \in \bb{Z} _ q.
The Chaum-Pederson protocol for the relation
\mc{R} = \bigg\lbrace \big( \beta, (u, v, w) \big) \in \bb{Z} _ q \times G^3 : v = g^\beta \land w = u^\beta \bigg\rbrace
goes as follows.
Pcomputes random\beta _ t \la \bb{Z} _ qand sends commitmentv _ t \la g^{\beta _ t},w _ t \la u^{\beta _ t}toV.Vcomputes challengec \la \mc{C}and sends it toP.Pcomputes\beta _ z \la \beta _ t + \beta c, and sends it toV.Voutputs\texttt{accept}if and only ifg^{\beta _ z} = v _ t \cdot v^candu^{\beta _ z} = w _ t \cdot w^c.
Completeness is obvious.
Theorem. The Chaum-Pedersen protocol provides special soundness and is special HVZK.
Proof. Also similar. See Theorem 19.10.2
This can be used to prove that an ElGamal ciphertext c = (u, v) = (g^k, h^k \cdot m) is an encryption of m with public key h = g^\alpha, without revealing the private key or the ephemeral key k. If (g^k, h^k \cdot m) is a valid ciphertext, then (h, u, vm^{-1}) = (g^\alpha, g^k, g^{\alpha k}) is a valid DH-triple.
Sigma Protocol for Arbitrary Linear Relations
Schnorr, Okamoto, Chaum-Pedersen protocols look similar. They are special cases of a generic sigma protocol for proving a linear relation among group elements. Read more in Section 19.5.3.2
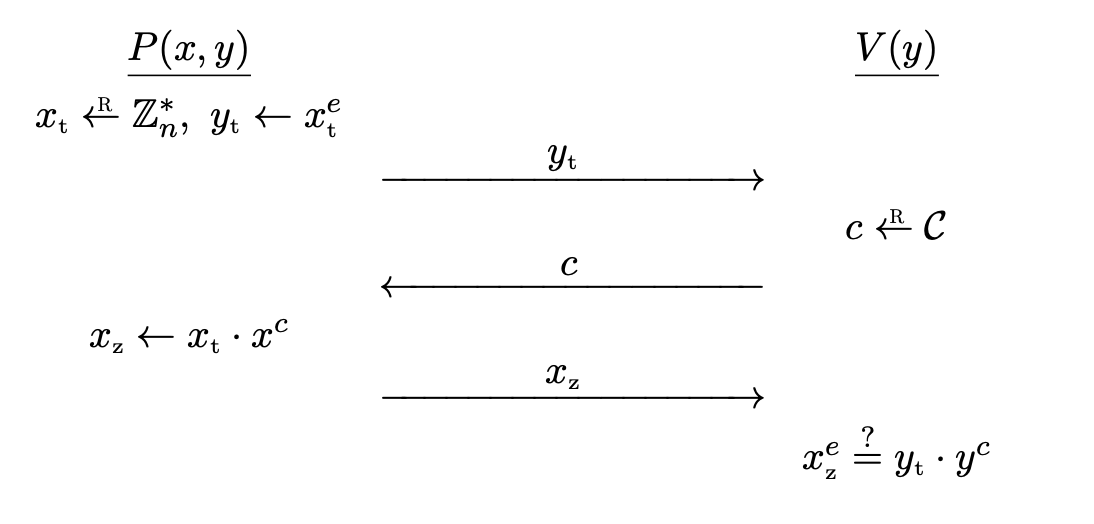
Sigma Protocol for RSA
Let (n, e) be an RSA public key, where e is prime. The Guillou-Quisquater (GQ) protocol is used to convince a verifier that he knows an $e$-th root of y \in \bb{Z} _ n^{\ast}.
The Guillou-Quisquater protocol for the relation
\mc{R} = \bigg\lbrace (x, y) \in \big( \bb{Z} _ n^{\ast} \big)^2 : x^e = y \bigg\rbrace
goes as follows.
Pcomputes randomx _ t \la \bb{Z} _ n^{\ast}and sends commitmenty _ t \la x _ t^etoV.Vcomputes challengec \la \mc{C}and sends it toP.Pcomputesx _ z \la x _ t \cdot x^cand sends it toV.Voutputs\texttt{accept}if and only ifx _ z^e = y _ t \cdot y^c.
Completeness is obvious.
Theorem. The GQ protocol provides special soundness and is special HVZK.
Proof. Also similar. See Theorem 19.13.2
Combining Sigma Protocols
Using the basic sigma protocols, we can build sigma protocols for complex statements.
AND-Proof Construction
The construction is straightforward, since we can just prove both statements.
Given two sigma protocols (P _ 0, V _ 0) for \mc{R} _ 0 \subset \mc{X} _ 0 \times \mc{Y} _ 0 and (P _ 1, V _ 1) for \mc{R} _ 1 \subset \mc{X} _ 1 \times \mc{Y} _ 1, we construct a sigma protocol for the relation \mc{R} _ \rm{AND} defined on (\mc{X} _ 0 \times \mc{X} _ 1) \times (\mc{Y} _ 0 \times \mc{Y} _ 1) as
\mc{R} _ \rm{AND} = \bigg\lbrace \big( (x _ 0, x _ 1), (y _ 0, y _ 1) \big) : (x _ 0, y _ 0) \in \mc{R} _ 0 \land (x _ 1, y _ 1) \in \mc{R} _ 1 \bigg\rbrace.
Given a pair of statements (y _ 0, y _ 1) \in \mc{Y} _ 0 \times \mc{Y} _ 1, the prover tries to convince the verifier that he knows a proof (x _ 0, x _ 1) \in \mc{X} _ 0 \times \mc{X} _ 1. This is equivalent to proving the AND of both statements.
PrunsP _ i(x _ i, y _ i)to get a commitmentt _ i.(t _ 0, t _ 1)is sent toV.Vcomputes challengec \la Cand sends it toP.Puses the challenge for bothP _ 0, P _ 1, obtains responsez _ 0,z _ 1, which is sent toV.Voutputs\texttt{accept}if and only if(t _ i, c, z _ i)is an accepting conversation fory _ i.
Completeness is clear.
Theorem. If
(P _ 0, V _ 0)and(P _ 1, V _ 1)provide special soundness and are special HVZK, then the AND protocol(P, V)defined above also provides special soundness and is special HVZK.
Proof. For special soundness, let \rm{Ext} _ 0, \rm{Ext} _ 1 be the knowledge extractor for (P _ 0, V _ 0) and (P _ 1, V _ 1), respectively. Then the knowledge extractor \rm{Ext} for (P, V) can be constructed straightforward. For statements (y _ 0, y _ 1), suppose that \big( (t _ 0, t _ 1), c, (z _ 0, z _ 1) \big) and \big( (t _ 0, t _ 1), c', (z _ 0', z _ 1') \big) are two accepting conversations. Feed \big( y _ 0, (t _ 0, c, z _ 0), (t _ 0, c', z _ 0') \big) to \rm{Ext} _ 0, and feed \big( y _ 1, (t _ 1, c, z _ 1), (t _ 1, c', z _ 1') \big) to \rm{Ext} _ 1.
For special HVZK, let \rm{Sim} _ 0 and \rm{Sim} _ 1 be simulators for each protocol. Then the simulator \rm{Sim} for (P, V) is built by using (t _ 0, z _ 0) \la \rm{Sim} _ 0(y _ 0, c) and (t _ 1, z _ 1) \la \rm{Sim} _ 1(y _ 1, c). Set
\big( (t _ 0, t _ 1), (z _ 0, z _ 1) \big) \la \rm{Sim}\big( (y _ 0, y _ 1), c \big).
We have used the fact that the challenge is used for both protocols.
OR-Proof Construction
However, OR-proof construction is difficult. The prover must convince the verifier that either one of the statement is true, but should not reveal which one is true.
If the challenge is known in advance, the prover can cheat. We exploit this fact. For the proof of y _ 0 \lor y _ 1, do the real proof for y _ b and cheat for y _ {1-b}.
Suppose we are given two sigma protocols (P _ 0, V _ 0) for \mc{R} _ 0 \subset \mc{X} _ 0 \times \mc{Y} _ 0 and (P _ 1, V _ 1) for \mc{R} _ 1 \subset \mc{X} _ 1 \times \mc{Y} _ 1. We assume that these both use the same challenge space, and both are special HVZK with simulators \rm{Sim} _ 0 and \rm{Sim} _ 1.
We combine the protocols to form a sigma protocol for the relation \mc{R} _ \rm{OR} defined on \big( \braces{0, 1} \times (\mc{X} _ 0 \cup \mc{X} _ 1) \big) \times (\mc{Y} _ 0\times \mc{Y} _ 1) as
\mc{R} _ \rm{OR} = \bigg\lbrace \big( (b, x), (y _ 0, y _ 1) \big): (x, y _ b) \in \mc{R} _ b\bigg\rbrace.
Here, b denotes the actual statement y _ b to prove. For y _ {1-b}, we cheat.
Pis initialized with\big( (b, x), (y _ 0, y _ 1) \big) \in \mc{R} _ \rm{OR}andVis initialized with(y _ 0, y _ 1) \in \mc{Y} _ 0 \times \mc{Y} _ 1. Letd = 1 - b.
Pcomputesc _ d \la \mc{C}and(t _ d, z _ d) \la \rm{Sim} _ d(y _ d, c _ d).PrunsP _ b(x, y _ b)to get a real commitmentt _ band sends(t _ 0, t _ 1)toV.Vcomputes challengec \la Cand sends it toP.Pcomputesc _ b \la c \oplus c _ d, feeds it toP _ b(x, y _ b)obtains a responsez _ b.Psends(c _ 0, z _ 0, z _ 1)toV.Vcomputesc _ 1 \la c \oplus c _ 0, and outputs\texttt{accept}if and only if(t _ 0, c _ 0, z _ 0)is an accepting conversation fory _ 0and(t _ 1, c _ 1, z _ 1)is an accepting conversation fory _ 1.
Step 1 is the cheating part, where the prover chooses a challenge, and generates a commitment and a response from the simulator.
Completeness follows from the following.
c _ b = c \oplus c _ {1-b}, soc _ 1 = c \oplus c _ 0always holds.- Both conversations
(t _ 0, c _ 0, z _ 0)and(t _ 1, c _ 1, z _ 1)are accepted.- An actual proof is done for statement
y _ b. - For statement
y _ {1-b}, the simulator always outputs an accepting conversation.
- An actual proof is done for statement
c _ b = c \oplus c _ d is random, so P cannot manipulate the challenge. Also, V checks c _ 1 = c \oplus c _ 0.
Theorem. If
(P _ 0, V _ 0)and(P _ 1, V _ 1)provide special soundness and are special HVZK, then the OR protocol(P, V)defined above also provides special soundness and is special HVZK.
Proof. For special soundness, suppose that \rm{Ext} _ 0 and \rm{Ext} _ 1 are knowledge extractors. Let
\big( (t _ 0, t _ 1), c, (c _ 0, z _ 0, z _ 1) \big), \qquad \big( (t _ 0, t _ 1), c', (c _ 0', z _ 0', z _ 1') \big)
be two accepting conversations with c \neq c'. Define c _ 1 = c \oplus c _ 0 and c _ 1' = c' \oplus c _ 0'. Since c \neq c', it must be the case that either c _ 0 \neq c _ 0' or c _ 1 \neq c _ 1'. Now \rm{Ext} will work as follows.
- If
c _ 0 \neq c _ 0', output\bigg( 0, \rm{Ext} _ 0\big( y _ 0, (t _ 0, c _ 0, z _ 0), (t _ 0, c _ 0', z _ 0') \big) \bigg). - If
c _ 1 \neq c _ 1', output\bigg( 1, \rm{Ext} _ 1\big( y _ 1, (t _ 1, c _ 1, z _ 1), (t _ 1, c _ 1', z _ 1') \big) \bigg).
Then \rm{Ext} will extract the knowledge.
For special HVZK, define c _ 0 \la \mc{C}, c _ 1 \la c \oplus c _ 0. Then run each simulator to get
(t _ 0, z _ 0) \la \rm{Sim} _ 0(y _ 0, c _ 0), \quad (t _ 1, z _ 1) \la \rm{Sim} _ 1(y _ 1, c _ 1).
Then the simulator for (P, V) outputs
\big( (t _ 0, t _ 1), (c _ 0, z _ 0, z _ 1) \big) \la \rm{Sim}\big( (y _ 0, y _ 1), c \big).
The simulator just simulates for both of the statements and returns the messages as in the protocol. c _ b is random, and the remaining values have the same distribution since the original two protocols were special HVZK.
Example: OR of Sigma Protocols with Schnorr Protocol
Let G = \left\langle g \right\rangle be a cyclic group of prime order q. The prover wants to convince the verifier that he knows the discrete logarithm of either h _ 0 or h _ 1 in G.
Suppose that the prover knows x _ b \in \bb{Z} _ q such that g^{x _ b} = h _ b.
- Choose
c _ {1-b} \la \mc{C}and call simulator of1-bto obtain(u _ {1-b}, z _ {1-b}) \la \rm{Sim} _ {1-b}.Psends two commitmentsu _ 0, u _ 1. - Foru _ b, choose randomy \la \bb{Z} _ qand setu _ b = g^y. - Foru _ {1-b}, use the value from the simulator.Vsends a single challengec \la \mc{C}.- Using
c _ {1-b}, split the challenge intoc _ 0,c _ 1so that they satisfyc _ 0 \oplus c _ 1 = c. Then send(c _ 0, c _ 1, z _ 0, z _ 1)toV. - Forz _ b, calculatez _ b \la y + c _ b x. - Forz _ {1-b}, use the value from the simulator.Vchecks ifc = c _ 0 \oplus c _ 1.Vaccepts if and only if(u _ 0, c _ 0, z _ 0)and(u _ 1, c _ 1, z _ 1)are both accepting conversations.
- Since
c, c _ {1-b}are random,c _ bis random. Thus one of the proofs must be valid.
Generalized Constructions
See Exercise 19.26 and 19.28.2
Non-interactive Proof Systems
Sigma protocols are interactive proof systems, but we can convert them into non-interactive proof systems using the Fiat-Shamir transform.
First, the definition of non-interactive proof systems.
Definition. Let
\mc{R} \subset \mc{X} \times \mc{Y}be an effective relation. A non-interactive proof system for\mc{R}is a pair of algorithms(G, V)satisfying the following.
Gis an efficient probabilistic algorithm that generates the proof as\pi \la G(x, y)for(x, y) \in \mc{R}.\pibelongs to some proof space\mc{PS}.Vis an efficient deterministic algorithm that verifies the proof asV(y, \pi)wherey \in \mc{Y}and\pi \in \mc{PS}.Voutputs either\texttt{accept}or\texttt{reject}. IfVoutputs\texttt{accept},\piis a valid proof fory.For all
(x, y) \in \mc{R}, the output ofG(x, y)must be a valid proof fory.
Non-interactive Soundness
Intuitively, it is hard to create a valid proof of a false statement.
Definition. Let
\Phi = (G, V)be a non-interactive proof system for\mc{R} \subset \mc{X} \times \mc{Y}with proof space\mc{PS}. An adversary\mc{A}outputs a statementy^{\ast} \in \mc{Y}and a proof\pi^{\ast} \in \mc{PS}to attack\Phi.The adversary wins if
V(y^{\ast}, \pi^{\ast}) = \texttt{accept}andy^{\ast} \notin L _ \mc{R}. The advantage of\mc{A}with respect to\Phiis defined as the probability that\mc{A}wins, and is denoted as\rm{Adv} _ {\rm{niSnd}}[\mc{A}, \Phi].If the advantage is negligible for all efficient adversaries
\mc{A},\Phiis sound.
Non-interactive Zero Knowledge
Omitted.
The Fiat-Shamir Transform
The basic idea is using a hash function to derive a challenge, instead of a verifier. Now the only job of the verifier is checking the proof, requiring no interaction for the proof.
Definition. Let
\Pi = (P, V)be a sigma protocol for a relation\mc{R} \subset \mc{X} \times \mc{Y}. Suppose that conversations(t, c, z) \in \mc{T} \times \mc{C} \times \mc{Z}. LetH : \mc{Y} \times \mc{T} \rightarrow \mc{C}be a hash function.Define the Fiat-Shamir non-interactive proof system
\Pi _ \rm{FS} = (G _ \rm{FS}, V _ \rm{FS})with proof space\mc{PS} = \mc{T} \times \mc{Z}as follows.
- For input
(x, y) \in \mc{R},G _ \rm{FS}runsP(x, y)to obtain a commitmentt \in \mc{T}. Then computes the challengec = H(y, t), which is fed toP(x, y), obtaining a responsez \in \mc{Z}.G _ \rm{FS}outputs(t, z) \in \mc{T} \times \mc{Z}.- For input
\big( y, (t, z) \big) \in \mc{Y} \times (\mc{T} \times \mc{Z}),V _ \rm{FS}verifies that(t, c, z)is an accepting conversation fory, wherec = H(y, t).
Any sigma protocol can be converted into a non-interactive proof system. Its completeness is automatically given by the completeness of the sigma protocol.
By modeling the hash function as a random oracle, we can show that:
- If the sigma protocol is sound, then so is the non-interactive proof system.3
- If the sigma protocol is special HVZK, then running the non-interactive proof system does not reveal any information about the secret.
Implications
- No interactions are required, resulting in efficient protocols with lower round complexity.
- No need to consider dishonest verifiers, since prover chooses the challenge. The verifier only verifies.
- In distributed systems, a single proof can be used multiple times.
Soundness of the Fiat-Shamir Transform
Theorem. Let
\Pibe a sigma protocol for a relation\mc{R} \subset \mc{X} \times \mc{Y}, and let\Pi _ \rm{FS}be the Fiat-Shamir non-interactive proof system derived from\Piwith hash functionH. If\Piis sound andHis modeled as a random oracle, then\Pi _ \rm{FS}is also sound.Let
\mc{A}be a $q$-query adversary attacking the soundness of\Pi _ \rm{FS}. There exists an adversary\mc{B}attacking the soundness of\Pisuch that\rm{Adv} _ {\rm{niSnd^{ro}}}[\mc{A}, \Pi _ \rm{FS}] \leq (q + 1) \rm{Adv} _ {\rm{Snd}}[\mc{B}, \Pi].
Proof Idea. Suppose that \mc{A} produces a valid proof (t^{\ast}, z^{\ast}) on a false statement y^{\ast}. Without loss of generality, \mc{A} queries the random oracle at (y^{\ast}, t^{\ast}) within q+1 queries. Then \mc{B} guesses which of the q+1 queries is the relevant one. If \mc{B} guesses the correct query, the conversation (t^{\ast}, c, z^{\ast}) will be accepted and \mc{B} succeeds. The factor q+1 comes from the choice of \mc{B}.
Zero Knowledge of the Fiat-Shamir Transform
Omitted. Works...
The Fiat-Shamir Signature Scheme
Now we understand why the Schnorr signature scheme used hash functions. In general, the Fiat-Shamir transform can be used to convert sigma protocols into signature schemes.
We need 3 building blocks.
- A sigma protocol
(P, V)with conversations of the form(t, c, z). - A key generation algorithm
Gfor\mc{R}, that outputspk = y,sk = (x, y) \in \mc{R}. - A hash function
H : \mc{M} \times \mc{T} \rightarrow \mc{C}, modeled as a random oracle.
Definition. The Fiat-Shamir signature scheme derived from
Gand(P, V)works as follows.
- Key generation: invoke
Gso that(pk, sk) \la G().
pk = y \in \mc{Y}andsk = (x, y) \in \mc{R}.- Sign: for message
m \in \mc{M}
- Start the prover
P(x, y)and obtain the commitmentt \in \mc{T}.- Compute the challenge
c \la H(m, t).cis fed to the prover, which outputs a responsez.- Output the signature
\sigma = (t, z) \in \mc{T} \times \mc{Z}.- Verify: with the public key
pk = y, computec \la H(m, t)and check that(t, c, z)is an accepting conversation foryusingV(y).
If an adversary can come up with a forgery, then the underlying sigma protocol is not secure.
Example: Voting Protocol
n voters are casting a vote, either 0 or 1. At the end, all voters learn the sum of the votes, but we want to keep the votes secret for each party.
We can use the multiplicative ElGamal encryption scheme in this case. Assume that a trusted vote tallying center generates a key pair, keeps sk = \alpha to itself and publishes pk = g^\alpha.
Each voter encrypts the vote b _ i and the ciphertext is
(u _ i, v _ i) = (g^{\beta _ i}, h^{\beta _ i} \cdot g^{b _ i})
where \beta _ i \la\bb{Z} _ q. The vote tallying center aggregates all ciphertexts my multiplying everything. No need to decrypt yet. Then
(u^{\ast}, v^{\ast}) = \left( \prod _ {i=1}^n g^{\beta _ i}, \prod _ {i=1}^n h^{\beta _ i} \cdot g^{b _ i} \right) = \big( g^{\beta^{\ast}}, h^{\beta^{\ast}} \cdot g^{b^{\ast}} \big),
where \beta^{\ast} = \sum _ {i=1}^n \beta _ i and b^{\ast} = \sum _ {i=1}^n b _ i. Now decrypt (u^{\ast}, v^{\ast}) and publish the result b^{\ast}.4
Since the ElGamal scheme is semantically secure, the protocol is also secure if all voters follow the protocol. But a dishonest voter can encrypt b _ i = -100 or some arbitrary value.
To fix this, we can make each voter prove that the vote is valid. Using the Chaum-Pedersen protocol for DH-triples and the OR-proof construction, the voter can submit a proof that the ciphertext is either a encryption of b _ i = 0 or 1. We can also apply the Fiat-Shamir transform here for efficient protocols, resulting in non-interactive proofs.
-
The message flows in a shape that resembles the greek letter
\Sigma, hence the name sigma protocol. ↩︎ -
A Graduate Course in Applied Cryptography. ↩︎
-
The challenge is chosen after the commitment, making it random. ↩︎
-
To find
b^{\ast}, one has to solve the discrete logarithm, but for realisticn, we can brute force this. ↩︎