* [PUBLISHER] upload files #175 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-19-symmetric-key-encryption.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #177 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-19-symmetric-key-encryptio.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #178 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #179 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #180 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #181 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #182 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #183 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #184 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #185 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #186 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #187 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 14. Secure Multiparty Computation.md * DELETE FILE : _posts/Lecture Notes/Modern Cryptography/2023-09-19-symmetric-key-encryption.md * DELETE FILE : _posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography/2023-09-18-symmetric-key-cryptography-2.md * [PUBLISHER] upload files #188 * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 14. Secure Multiparty Computation.md * DELETE FILE : _posts/Lecture Notes/Modern Cryptography/2023-09-19-symmetric-key-encryption.md * chore: remove files * [PUBLISHER] upload files #197 * PUSH NOTE : 수학 공부에 대한 고찰.md * PUSH NOTE : 09. Lp Functions.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-09.png * PUSH NOTE : 08. Comparison with the Riemann Integral.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-08.png * PUSH NOTE : 04. Measurable Functions.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-04.png * PUSH NOTE : 06. Convergence Theorems.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-06.png * PUSH NOTE : 07. Dominated Convergence Theorem.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-07.png * PUSH NOTE : 05. Lebesgue Integration.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-05.png * PUSH NOTE : 03. Measure Spaces.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-03.png * PUSH NOTE : 02. Construction of Measure.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-02.png * PUSH NOTE : 01. Algebra of Sets and Set Functions.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mt-01.png * PUSH NOTE : Rules of Inference with Coq.md * PUSH NOTE : 블로그 이주 이야기.md * PUSH NOTE : Secure IAM on AWS with Multi-Account Strategy.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : separation-by-product.png * PUSH NOTE : You and Your Research, Richard Hamming.md * PUSH NOTE : 10. Digital Signatures.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-10-dsig-security.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-10-schnorr-identification.png * PUSH NOTE : 9. Public Key Encryption.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-09-ss-pke.png * PUSH NOTE : 8. Number Theory.md * PUSH NOTE : 7. Key Exchange.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-07-dhke.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-07-dhke-mitm.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-07-merkle-puzzles.png * PUSH NOTE : 6. Hash Functions.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-06-merkle-damgard.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-06-davies-meyer.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-06-hmac.png * PUSH NOTE : 5. CCA-Security and Authenticated Encryption.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-05-ci.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-05-etm-mte.png * PUSH NOTE : 1. OTP, Stream Ciphers and PRGs.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-01-prg-game.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-01-ss.png * PUSH NOTE : 4. Message Authentication Codes.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-04-mac.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-04-mac-security.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-04-cbc-mac.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-04-ecbc-mac.png * PUSH NOTE : 3. Symmetric Key Encryption.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-03-ecb-encryption.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-03-cbc-encryption.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-03-ctr-encryption.png * PUSH NOTE : 2. PRFs, PRPs and Block Ciphers.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-02-block-cipher.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-02-feistel-network.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-02-des-round.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-02-DES.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-02-aes-128.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-02-2des-mitm.png * PUSH NOTE : 18. Bootstrapping & CKKS.md * PUSH NOTE : 17. BGV Scheme.md * PUSH NOTE : 16. The GMW Protocol.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-16-beaver-triple.png * PUSH NOTE : 15. Garbled Circuits.md * PUSH NOTE : 14. Secure Multiparty Computation.md * PUSH NOTE : 13. Sigma Protocols.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-13-sigma-protocol.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-13-okamoto.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-13-chaum-pedersen.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-13-gq-protocol.png * PUSH NOTE : 12. Zero-Knowledge Proofs (Introduction).md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : mc-12-id-protocol.png * PUSH NOTE : 11. Advanced Topics.md * PUSH NOTE : 0. Introduction.md * PUSH NOTE : 02. Symmetric Key Cryptography (1).md * PUSH NOTE : 09. Transport Layer Security.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-09-tls-handshake.png * PUSH NOTE : 08. Public Key Infrastructure.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-08-certificate-validation.png * PUSH NOTE : 07. Public Key Cryptography.md * PUSH NOTE : 06. RSA and ElGamal Encryption.md * PUSH NOTE : 05. Modular Arithmetic (2).md * PUSH NOTE : 03. Symmetric Key Cryptography (2).md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-03-feistel-function.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-03-cfb-encryption.png * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-03-ofb-encryption.png * PUSH NOTE : 04. Modular Arithmetic (1).md * PUSH NOTE : 01. Security Introduction.md * PUSH ATTACHMENT : is-01-cryptosystem.png * PUSH NOTE : Search Time in Hash Tables.md * PUSH NOTE : 랜덤 PS일지 (1).md * chore: rearrange articles * feat: fix paths * feat: fix all broken links * feat: title font to palatino
15 KiB
share, toc, math, categories, path, tags, title, date, github_title, image, attachment
| share | toc | math | categories | path | tags | title | date | github_title | image | attachment | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| true | true | true |
|
_posts/lecture-notes/modern-cryptography |
|
4. Message Authentication Codes | 2023-09-21 | 2023-09-21-macs |
|
|
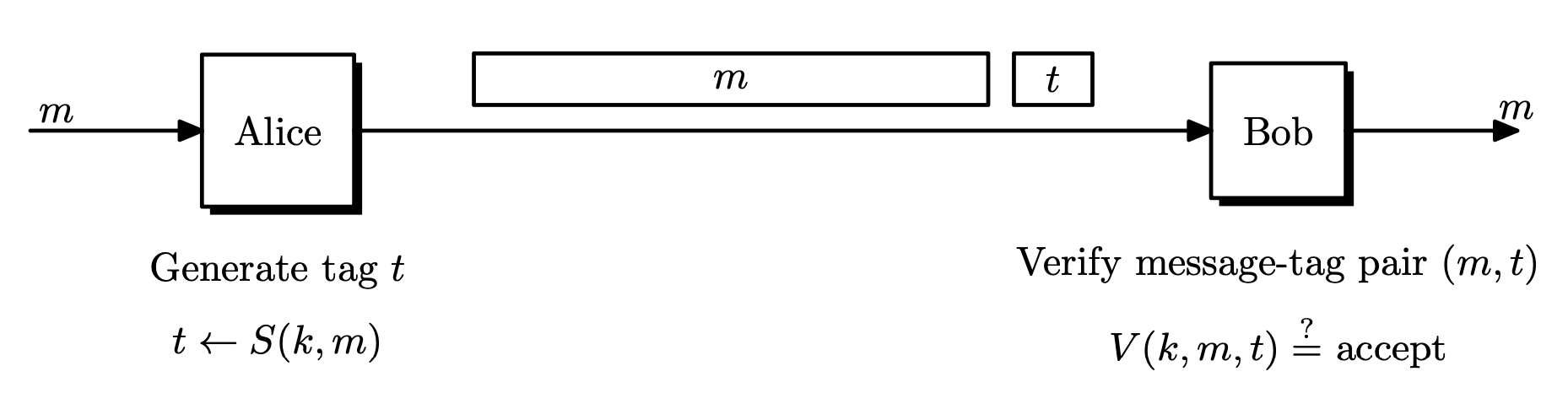
Message authentication codes (MAC) were designed to provide message integrity. Bob receives a message from Alice and wants to know if this message was not modified during transmission. For MACs, the message itself does not have to be secret. For example, when we download a file the file itself does not have to be protected, but we need a way to verify that the file was not modified.
Note that MAC is different from error correcting codes (ECC). ECC fixes accidental errors. For example, the Ethernet protocol uses CRC32, which is keyless. Keyless integrity mechanisms are designed to detect and fix random transmission errors, and the adversary can easily modify the data since there is no key and the algorithm is publicly known.
On the other hand, MAC fixes data that is tampered in purpose. We will also require a key so that the adversary cannot easily modify the message. We assume that the secret key is shared between two parties, in advance.
Message Authentication Code
Definition. A MAC system
\Pi = (S, V)defined over(\mathcal{K}, \mathcal{M}, \mathcal{T})is a pair of efficient algorithmsSandVwhereSis a signing algorithm andVis a verification algorithm.
S : \mathcal{K} \times \mathcal{M} \rightarrow \mathcal{T}is a probabilistic algorithm that outputst \leftarrow S(k, m)for some keyk \in \mathcal{K}and messagem \in \mathcal{M}. The outputtis called a tag, and\mathcal{T}is the tag space.V: \mathcal{K} \times \mathcal{M} \times \mathcal{T} \rightarrow \left\lbrace 0, 1 \right\rbraceis a deterministic algorithm that computesV(k, m, t)and outputs1(\texttt{accept}) or0(\texttt{reject}) .- It is required that
V(k, m, S(k, m)) = 1.
When V accepts (m, t), then t is called a valid tag. Since (m, t) is the transmitted data, we want t to be short as possible.
Canonical Verification
V can be replaced with an invocation of S if S is deterministic. The receiver can recompute the tag and check equality.
V(k, m, t) = 1 \iff t = S(k, m)
This is called canonical verification. All real-world MACs use canonical verification.
Secure MAC: Unforgeability
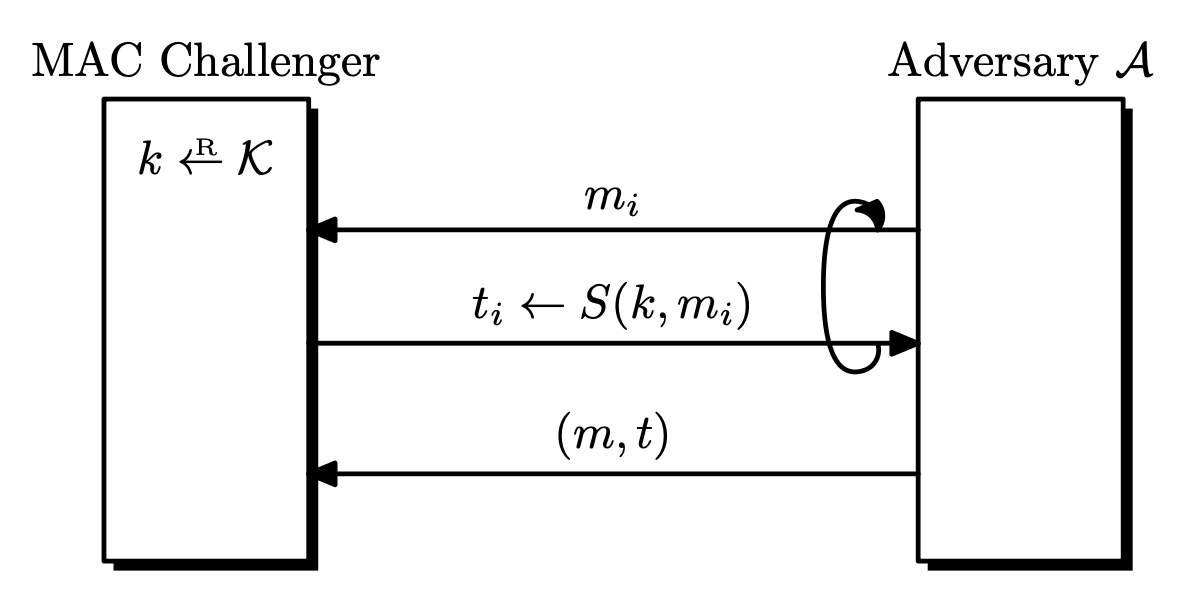
In the security definition of MACs, we allow the attacker to request tags for arbitrary messages of its choice, called chosen-message attacks. This assumption will allow the attacker to collect a bunch of valid (m, t) pairs. In this setting, we require the attacker to forge a new valid message-tag pair, which is different from what the attacker has. Also, it is not required that the forged message m have any meaning. This is called existential forgery. A MAC system is secure if an existential forgery is almost impossible. Note that we are giving the adversary much power in the definition, to be conservative.
- Attacker is given
t _ i \leftarrow S(k, m _ i)form _ 1, \dots, m _ qof his choice.- Attacker has a signing oracle.
- Attacker's goal is existential forgery.
- MAC: generate a new valid message-tag pair
(m, t)such thatV(k, m, t) = 1andm \notin \left\lbrace m _ 1, \dots, m _ q \right\rbrace. - Strong MAC: generate a new valid message-tag pair
(m, t)V(k, m, t) = 1and(m, t) \notin \left\lbrace (m _ 1, t _ 1), \dots, (m _ q, t _ q) \right\rbrace.
- MAC: generate a new valid message-tag pair
For strong MACs, the attacker only has to change the tag for the attack to succeed.
Definition. Let
\Pi = (S, V)be a MAC system defined over(\mathcal{K}, \mathcal{M}, \mathcal{T}). Given an adversary\mathcal{A}, the security game goes as follows.
- The challenger picks a random
k \leftarrow \mathcal{K}.\mathcal{A}queries the challengerqtimes. - The $i$-th signing query is a messagem _ i, and receivest _ i \leftarrow S(k, m _ i).\mathcal{A}outputs a new forged pair(m, t)that is not among the queried pairs. -m \notin \left\lbrace m _ 1, \dots,m _ q \right\rbrace-(m, t) \notin \left\lbrace (m _ 1, t _ 1), \dots, (m _ q, t _ q) \right\rbrace(for strong MAC)
\mathcal{A}wins if(m, t)is a valid pair underk. Let this event beW. The MAC advantage with respect to\Piis defined as\mathrm{Adv} _ {\mathrm{MAC}}[\mathcal{A}, \Pi] = \Pr[W]and a MAC
\Piis secure if the advantage is negligible for any efficient\mathcal{A}. In this case, we say that\Piis existentially unforgeable under a chosen message attack.
If a MAC is secure, the attacker learns almost nothing from the q queries. i.e, the tags for the previous q messages gives no useful information for producing a tag for some other message m, even in cases where messages are almost identical.
MAC Security with Verification Queries
The above definition can be modified to include verification queries, where the adversary \mathcal{A} queries (m _ j, t _ j) \in \mathcal{M} \times \mathcal{T} and the challenger responds with V(k, m _ j, t _ j). \mathcal{A} wins if any verification query is returned with 1 (\texttt{accept}).
It can be shown that for strong MACs, these two definitions are equivalent. See Theorem 6.1.1 For (just) MACs, these are not equivalent. See Exercise 6.7.1
Since these two definition are equivalent, security proofs are easier when we use the definition without verification queries.
Notes on the Security Definition
Replay Attacks
The definition requires that the adversary generate a new message-tag pair. In the real world, there are replay attacks that send the same message multiple times. For example, intercepting a bank transaction message and sending it several times can be critical. Replay attacks should be handled differently, by using sequence numbers in messages or by appending a timestamp.
Secure MAC with Canonical Verification
A secure MAC with canonical verification is strongly secure, since S is deterministic, so for every message m \in \mathcal{M}, there is a unique tag t \in \mathcal{T}. Thus it is impossible to only modify the tag.
MAC Constructions from PRFs
Block ciphers were actually PRPs, but we have a large message space, so by the PRF switching lemma, we can use block ciphers as PRFs and construct other systems!
Let
F : \mathcal{K} \times X \rightarrow Ybe a PRF. Define a MAC scheme\Pi = (S, V)over(\mathcal{K}, X, Y)as
S(k, m) = F(k, m)V(k, m, t) = 1ift = F(k, m)and0otherwise.
This MAC is derived from $F$, and is deterministic. This scheme is secure as long as \left\lvert Y \right\lvert is sufficiently large. This is necessary since if \left\lvert Y \right\lvert is small, then an adversary can randomly guess the tag with non-negligible probability.
Theorem. Let
F : \mathcal{K} \times X \rightarrow Ybe a secure PRF. If\left\lvert Y \right\lvertis sufficiently large, then\Piis a secure MAC.For every efficient MAC adversary
\mathcal{A}against\Pi, there exists an efficient PRF adversary\mathcal{B}such that\mathrm{Adv} _ {\mathrm{MAC}}[\mathcal{A}, \Pi] \leq \mathrm{Adv} _ {\mathrm{PRF}}[\mathcal{B}, F] + \frac{1}{\left\lvert Y \right\lvert}.
Proof. See Theorem 6.2.1
The above construction uses a PRF, so it is restricted to messages of fixed size. We also need a MAC for longer messages.
MAC Constructions for Fixed Length Messages
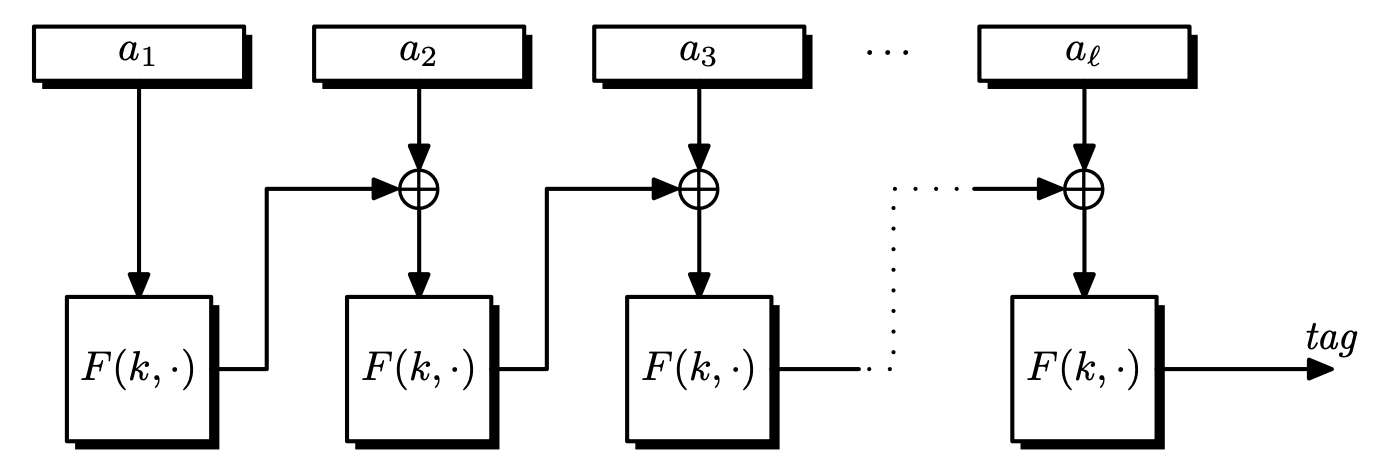
CBC-MAC
Definition. For any message
m = (m _ 0, m _ 1, \dots, m _ {l-1}) \in \left\lbrace 0, 1 \right\rbrace^{nl}, letF _ k := F(k, \cdot).S _ \mathrm{CBC}(m) = F _ k(F _ k(\cdots F _ k(F _ k(m _ 0) \oplus m _ 1) \oplus \cdots) \oplus m _ {l-1}).
S _ \mathrm{CBC} is similar to CBC mode encryption, but there is no intermediate output, and the IV is fixed as 0^n.
Theorem. If
F : \mathcal{K} \times \left\lbrace 0, 1 \right\rbrace^n \rightarrow \left\lbrace 0, 1 \right\rbrace^nis a secure PRF, then for a fixed $l$, CBC-MAC is secure for messages\mathcal{M} = \left\lbrace 0, 1 \right\rbrace^{nl}.
The following modifications show some of the ways that CBC-MAC could become insecure.
Using Shorter Messages is Insecure (Extension Attack)
For any messages shorter than nl, CBC-MAC is not secure. So the length of the messages should be fixed in advance by the sender and the receiver.
To see this, consider the following extension attack.
- Pick an arbitrary
m _ 0 \in \left\lbrace 0, 1 \right\rbrace^n. - Request the tag
t = F(k, m _ 0). - Set
m _ 1 = t \oplus m _ 0and output(m _ 0, m _ 1) \in \left\lbrace 0, 1 \right\rbrace^{2n}andtas the tag.
Then the verification works since
S _ \mathrm{CBC}(k, (m _ 0, t\oplus m _ 0)) = F(k, F(k, m _ 0) \oplus (t \oplus m _ 0)) = F(k, m _ 0) = t.
Random IV is Insecure
If we use random IV instead of 0^n, CBC-MAC is insecure. Suppose a random IV was chosen from \left\lbrace 0, 1 \right\rbrace^n and the final output was (\mathrm{IV}, t). Then the following attack is possible.
- Pick an arbitrary
m \in \left\lbrace 0, 1 \right\rbrace^n. - Request the tag
(\mathrm{IV}, t). (t = F(k, m)) - Send
m' = \mathrm{IV} \oplus mand tag(\mathrm{IV}, t).
Then the verification works since
S _ \mathrm{CBC}(k, \mathrm{IV} \oplus m) = F(k, (\mathrm{IV} \oplus m) \oplus \mathrm{IV}) = F(k, m) = t.
Disclosing Intermediate Values is Insecure
If CBC-MAC outputs all intermediate values of F(k, \cdot), then CBC-MAC is insecure. Consider the following attack.
- Pick an arbitrary
(m _ 0, m _ 1) \in \left\lbrace 0, 1 \right\rbrace^{2n}. - Request the computed values
(t _ 0, t), wheret _ 0 = F(k, m _ 0)andt = F(k, m _ 1 \oplus t _ 0). - Send
(m _ 0, m _ 0 \oplus t _ 0) \in \left\lbrace 0, 1 \right\rbrace^{2n}and tagt _ 0.
Then the verification works since
S _ \mathrm{CBC}(k, (m _ 0, m _ 0 \oplus t _ 0)) = F(k, F(k, m _ 0) \oplus (m _ 0 \oplus t _ 0)) = F(k, m _ 0) = t _ 0.
The lesson is that cryptographic constructions should be implemented exactly as it was specified, without any unproven variations.
CBC-MAC for Messages of Arbitrary Length
We can extend CBC-MAC for arbitrary length messages. First, assume that all messages have lengths divisible by n.
Length Prepending
We can prepend the length of message \left\lvert m \right\lvert, encoded as an $n$-bit string. The computation of CBC-MAC is the same. It can be shown that this MAC scheme is secure.
However, this cannot be used if the length of the message is not known in advance. Also, only prepending works since appending the length is not secure. See Exercise 6.8.1
Proposition. Appending the length of the message in CBC-MAC is insecure.
Proof. Let n be the length of a block. Query m _ 1, m _ 2, m _ 1 \parallel n \parallel m _ 3 and receive 3 tags, t _ 1 = E _ k(E _ k(m _ 1) \oplus n), t _ 2 = E _ k(E _ k(m _ 2) \oplus n), t _ 3 = E _ k(E _ k(t _ 1 \oplus m _ 3) \oplus 3n).
Now forge a message-tag pair (m _ 2 \parallel n \parallel (m _ 3 \oplus t _ 1 \oplus t _ 2), t _ 3). Then the tag is
E _ k(E _ k(\overbrace{E _ k(E _ k(m _ 2) \oplus n)}^{t _ 2} \oplus m _ 3 \oplus t _ 1 \oplus t _ 2) \oplus 3n) = E _ k(E _ k(t _ 1 \oplus m _ 3) \oplus 3n)
which equals t _ 3. Note that the same logic works if the length is anywhere in the message, except for the beginning.
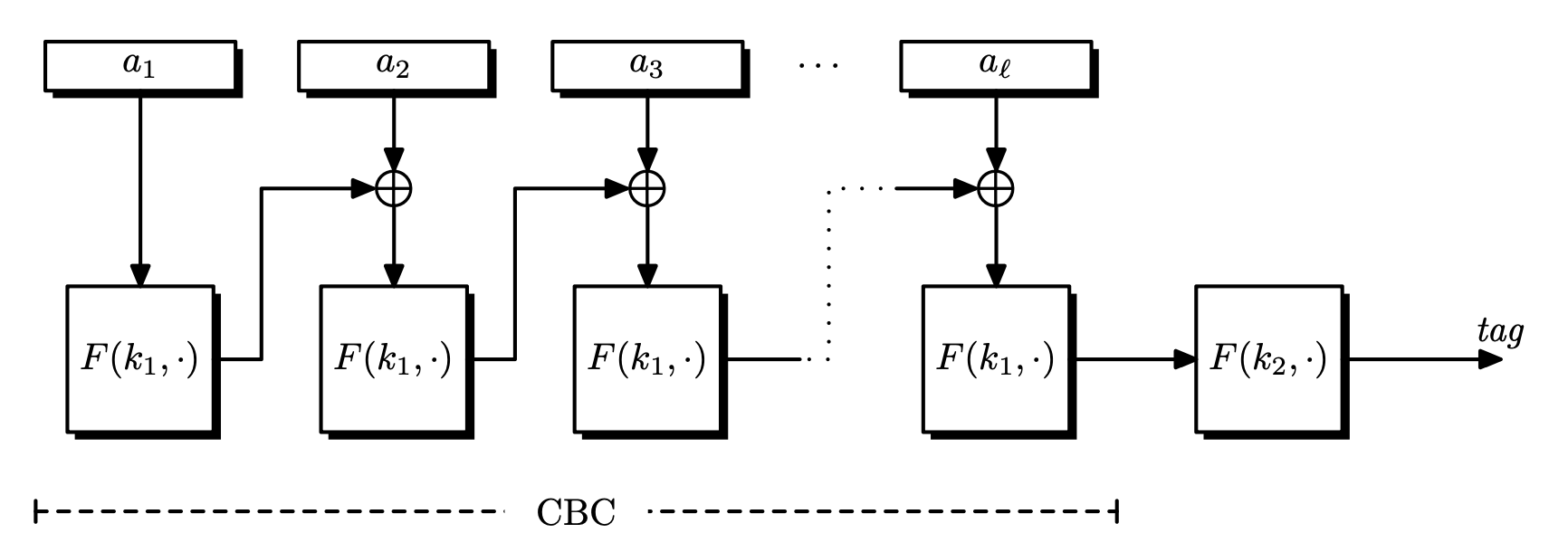
Encrypt Last Block (ECBC-MAC)
Since CBC-MAC is vulnerable to extension attacks, we encrypt the last block again. Choose a second key k' \in \mathcal{K} to encrypt the tag, so t' = F(k', t). This method is called encrypt-last-block CBC-MAC (ECBC-MAC).
ECBC-MAC doesn't require us to know the message length in advance, but it is relatively expensive in practice, since a block cipher has to be initialized with a new key.
Theorem. Let
F : \mathcal{K} \times X \rightarrow Xbe a secure PRF. Then for anyl \geq 0,F _ \mathrm{ECBC} : \mathcal{K}^2 \times X^{\leq l} \rightarrow Xis a secure PRF.For any efficient $q$-query PRF adversary
\mathcal{A}againstF _ \mathrm{ECBC}, there exists an efficient PRF adversary\mathcal{B}such that\mathrm{Adv} _ {\mathrm{PRF}}[\mathcal{A}, F _ \mathrm{ECBC}] \leq \mathrm{Adv} _ {\mathrm{PRF}}[\mathcal{B}, F] + \frac{2q^2l^2}{\left\lvert X \right\lvert}.
Thus ECBC-MAC is secure as long as ql \ll \sqrt{\left\lvert X \right\lvert}.
Extendable PRF
Definition. Let
PFbe a PRF defined over(\mathcal{K}, X^{\leq l}, Y).PFis extendable if for allk \in \mathcal{K},x, y \in X^{\leq l}anda \in X,PF(k, x) = PF(k, y) \implies PF(k, x \parallel a) = PF(k, y \parallel a).
It is easy to see that (E)CBC is an extendable PRF.
Attacking ECBC with \sqrt{\left\lvert X \right\lvert} Messages
- Make
q = \sqrt{\left\lvert X \right\lvert}queries using random messagesm _ i \in Xand obtaint _ i = F _ \mathrm{ECBC}(k, m _ i). - With a high probability, there is a collision
t _ i = t _ jfori \neq j. - Query for
m _ i \parallel mand receive the tagt. - Return a forged pair
(m _ j \parallel m, t).
This works because ECBC is an extendable PRF. t also works as a valid tag for m _ j \parallel m.
So ECBC becomes insecure after signing \sqrt{\left\lvert X \right\lvert} messages.
Bit-wise PRF Using Block-wise PRF
Now we construct a bitwise PRF, that enables us to sign messages of arbitrary length. We pad the messages so that they can be signed block-wise.
Specifically, pad with 1000\dots0. If the message length is already a multiple of n, then add a dummy block and pad with 1000\dots0. It is easy to see that this padding is injective, so using this padding gives us a secure PRF for bit-wise operations.
Other Constructions
- CMAC (OMAC)
- Simplified version of ECBC-MAC
- Uses only one key
- NIST standard
- Parallelizable MAC (PMAC)
- Uses two keys.
- Better than ECBC, since it is parallelizable.
- Each message block is XORed with a easy-to-compute function, then it is encrypted.
- All encrypted blocks are XORed, and finally encrypted again.
- PMAC is incremental: the tag can be easily updated when a message block changes.
- Hash-MAC (HMAC)